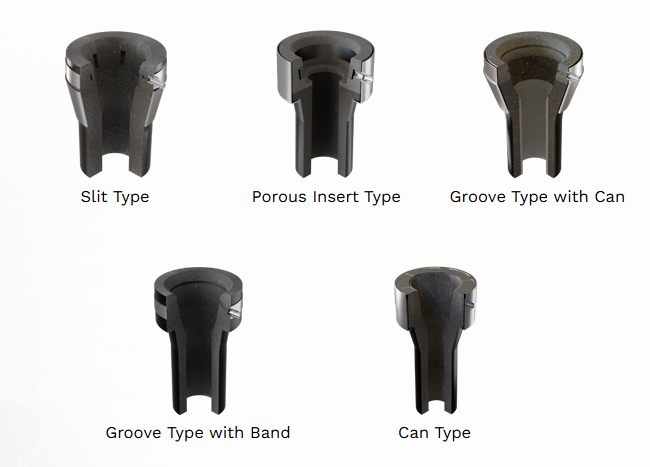
Tundish
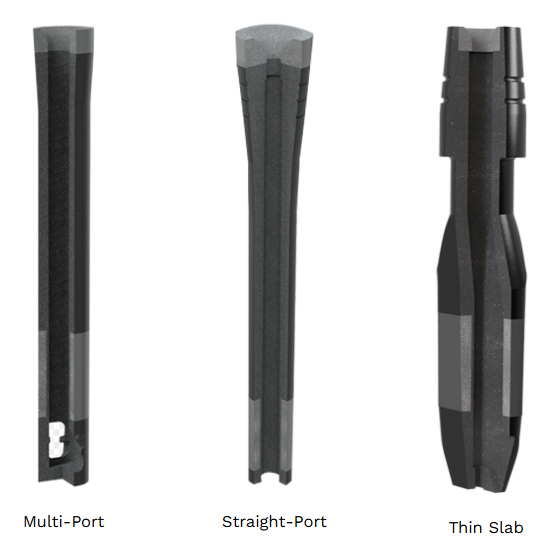
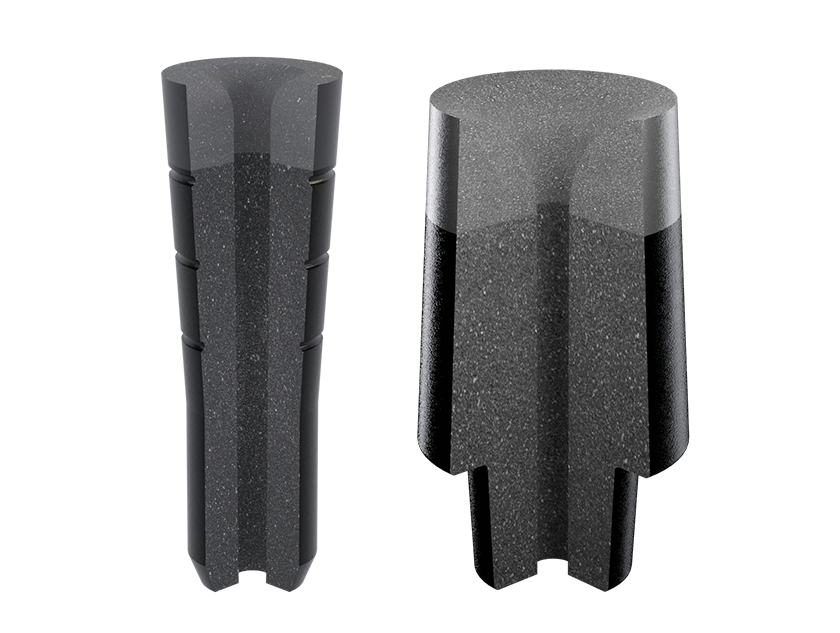
Sub Entry Nozzle (SEN)
The Sub Entry Nozzle / Shroud (SEN / SES / TCM-SES) is an iso-statically pressed refractory tube used to control the flow of molten steel from the tundish to the mould. Its primary function is to prevent re-oxidation of steel during transfer. The design of SEN / SES plays a critical role in the casting process by modulating steel flow and influencing the thermal characteristics inside the mould.
Know More
Click HereLadle Shroud (LS)
The Ladle Shroud (LS) is an iso-statically pressed refractory tube that ensures a controlled and protected flow of molten steel from the ladle to the tundish, minimising exposure to atmospheric oxygen. This significantly reduces re-oxidation, nitrogen pick-up, and inclusion formation, ensuring superior steel quality and consistent casting performance.
Know More
Click HereThin Slab SEN
It’s a specially designed SEN used to delivers molten steel from the tundish to thinner section mold under regulated conditions. The special shape SEN is used in advanced design funnel moulds of Slab caster of thickness varying from 50mm to 100mm.
Know More
Click HereTCM SES
In contrast to conventional slab casting systems, where the Submerged Entry Nozzle (SEN) limits casting sequences due to thermal and flow constraints, the SES with Tube Changing Mechanism (TCM-SES) is engineered to support extended casting sequences. This system enables smooth and safe changeover of TCM-SES, allowing long, uninterrupted casting operations.
Know More
Click HereTundish Nozzle (TN)
The Tundish Nozzle (TN) is an iso-statically pressed Alumina-Graphite refractory that serves as an intermediate component between the Monoblock Stopper (MBS) and the Sub Entry Shroud (SES). The stopper regulates the steel flow in conjunction with the TN. The TCM-TN/TN system, introduced as part of continuous casting refractories, enables hot changing of the Sub Entry Shroud for extended casting sequences.
Know More
Click HereBasic Ramming Mass
Magnesia-based ramming mass is a monolithic refractory material primarily composed of magnesia (MgO). It is widely used for lining furnaces, particularly in the steelmaking industry. This dry, bulk material is rammed into place during construction or repair, providing excellent resistance to high temperatures, thermal shock, and corrosion caused by molten metals and slags.
Magnesia ramming mass is produced using sintered or fused magnesia as the main component, combined with fine powders, binders, and sintering aids. It is installed by compacting (ramming) the material into place, either manually or with mechanical tools.
Know More
Click HereNeutral Ramming Mass
Neutral Ramming Mass (NRM) is a fused alumina–based refractory designed for lining coreless induction furnaces. Its unique three-layer structure delivers excellent mechanical properties and high-temperature strength.
Know More
Click HereMono Block Stopper (MBS)
The Monoblock Stopper (MBS) is an iso-statically pressed refractory component used to regulate the flow of steel from the tundish to the mould. Its advanced design helps maintain consistent mould levels, prevents vortex formation, and minimises inclusions—ensuring high-quality steel output.